

The issue of medical waste is increasingly relevant: the recent Covid-19 pandemic with its resulting economic consequences has underlined how crucial it is to have integrated and definitive solutions.
Hospitals and private healthcare facilities of all sizes are faced with complex and costly procedures for medical waste management.
The storage, transport, and treatment of infectious hospital waste constitute one the highest costs for the healthcare industry, both economically/financially and from an environmental standpoint.
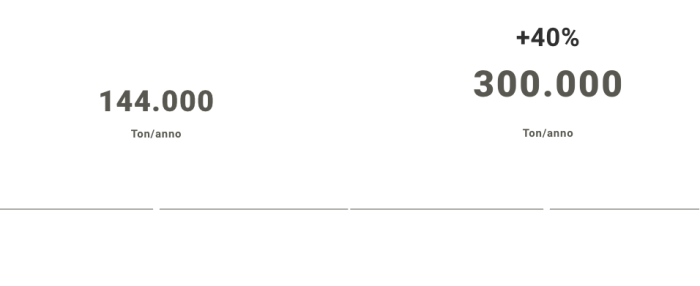
We are talking about a production of 144 thousand tons of waste per year in Italy alone. Following the Covid-19 pandemic, medical waste increased by 40% in 2020, up to 300 thousand tons/year. This growth is related to a higher number of hospital admissions and the use of PPEs, which has increased exponentially for well-known reasons.


Medical waste, and specifically infectious medical waste, has become a global emergency.
Most countries are developing new rules and guidelines to reduce the cost and environmental impact of infectious waste, paying special attention to the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Guidelines (SDGs).
Generally, new legislation has the following objectives:






The cumulative effect of these guidelines is pushing legislators to promote on-site medical waste sterilization and treatment.
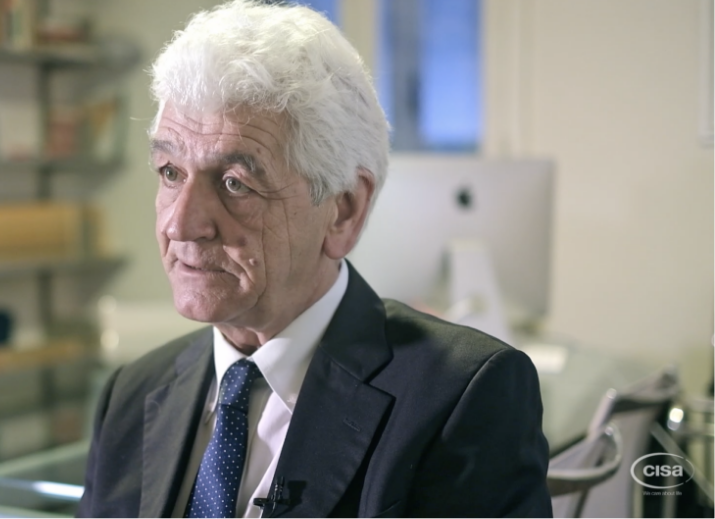
Cisa Group is leading the field with the invention of a Waste Sterile Department (WSD®), which is based on and adapts the principle of the CSSD , from which the new technology for medical waste treatment is directly derived.
The Italian legislature has recently introduced the Simplification for Medical Waste Management., and many other countries are introducing similar regulations.
The Italian Converted Into Law Decree 40/2020, in Art.30 Bis and the subsequent Italian Legislative Decree 76/2020, in Art.63 Bis, establish that medical waste at infectious risk only, subjected to sterilization procedures according to the provisions of Presidential Decree 254 “Medical Waste”, at public and private healthcare facilities, falls under the legal status of urban waste.
The concept of simplification for medical waste management is an important innovation: it means that medical waste, properly sterilized, can be disposed of as undifferentiated waste: without having to be sent to the incinerator, it can be treated as mixed municipal waste according to EWC 20 03 01.
In order to implement this smart management of infectious medical waste, the institution must equip itself with appropriate technology. Cisa WSD® allows for the application of this procedure in full compliance with regulations, with safe and environmentally friendly results.
1. |
CRITICAL ISSUES RELATED TO THE TRANSPORT OF MEDICAL WASTE
*In Italy, there were an estimated 200,000 special transports per year before the Covid-19 pandemic. |
2. |
OVERALL COST OF OPERATION |
3. |
CRITICAL ISSUES RELATED TO THE STORAGE OF INFECTIOUS MEDICAL WASTE
|
4. |
RESPONSIBILITY OF THE PRODUCER IN THE MANAGEMENT OF INFECTIOUS MEDICAL WASTE The responsibility of the producer is another sensitive issue related to the storage and treatment of infectious hospital waste. Waste legislation is quite complex in many cases, but on this issue it is clear and specific: hospitals and healthcare facilities are to be considered waste producers, with specific obligations and duties. The responsibility of the Institution or facility does not cease with the transfer to the disposal operator. In Italy, various laws and rulings reaffirm the principle of the waste chain: “the accountability and cooperation of all parties involved, in whatever capacity, not only in the waste management cycle, but also of the goods from which waste originates”. The authority/facility can therefore also be held co-responsible for disposal after the transfer. (Legislative Decree no. 152/2006, Ruling of the Criminal Court of Cassation April 10, 2012, n. 13363). The UK Environment Protection Act 1990 states that all waste producers have a Duty of Care to ensure the proper management of waste, “… the responsibility to take all reasonable steps to ensure that when transferring waste to another waste holder, the waste is properly managed throughout its entire journey to disposal or recovery”. Environment Agency Statutory Guidance. |
Management of infectious medical waste is a high cost item. The possibility of reducing the costs related to hospital waste management directly concerns Healthcare Managers and Hospitals.
According to research carried out by PWC Italia the average disposal cost of infectious medical waste (before the pandemic) was € 1.81 per kg with an estimated annual expenditure of € 270,000,000.
These numbers have dramatically increased since the Covid-19 pandemic.
The new Cisa Waste technology and the application of the simplified procedure for medical waste management provide high savings for the facility.
The on-site sterilization of medical waste makes it possible to transform large volumes of waste into small volumes, which can then be treated as mixed municipal waste (from EWC18.01.03 EWC18.02.02 to EWC 20 03 01).
As a result, benefits arise in terms of circular economy and financial management that are truly interesting for any healthcare facility.
Consequently, there are also economic savings due to simplified and faster handling of medical waste.
€ 0,86
Costo finale a kg
Ammortamento in anni: 7
kg/anno: 100.000
Giorni lavorativi: 250
Ore di attività giornaliera: 8
Staff impiegato: 1
€ 0,69
Costo finale a kg
Ammortamento in anni: 5
kg/anno: 140.000
Giorni lavorativi: 250
Ore di attività giornaliera: 8
Staff impiegato: 1
€ 0,50
Costo finale a kg
Ammortamento in anni: 5
kg/anno: 300.000
Giorni lavorativi: 250
Ore di attività giornaliera: 8
Staff impiegato: 1
€ 0,44
Costo finale a kg
Ammortamento in anni: 5
kg/anno: 800.000
Giorni lavorativi: 250
Ore di attività giornaliera: 12
Staff impiegato: 2

Reduction of waste volume
and hazardousness
Increased safety
for operators
Higher safeguard
of the producer’s responsibility

Econimic benefits

Reduced environmental impact

Maximum compliance with regulations
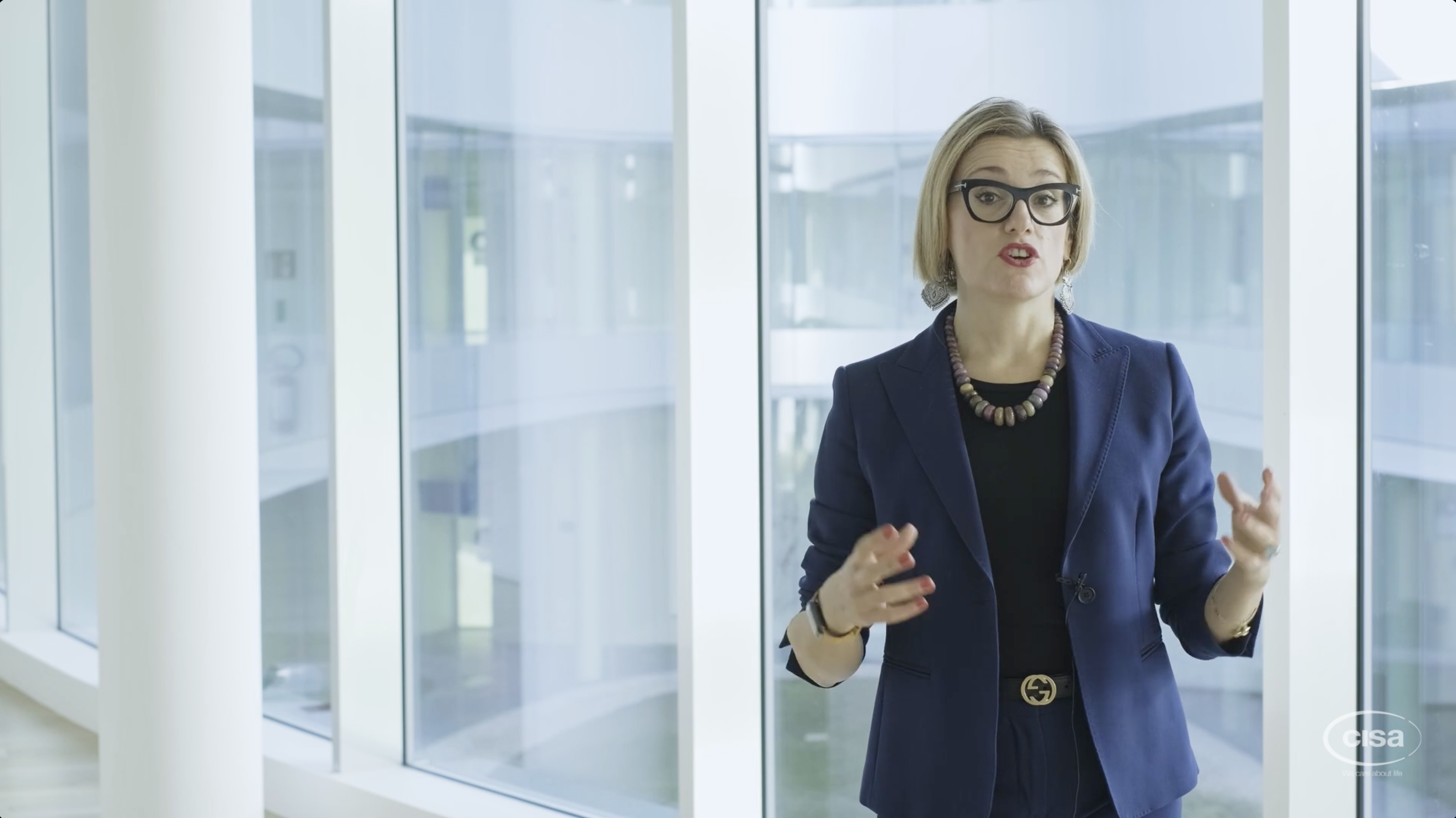
Cisa Production Srl has always been mindful of the planet’s problems and sensitive to sustainability issues related to the environment, consumption, and the safeguard of persons.
The development of the Cisa Group’s Waste technology for the treatment of hospital waste confirms this once again.
These are some of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for the 2030 roadmap that can be achieved through the implementation of WSD systems within healthcare facilities.




Volumes & costs reduction
Process control
Risk management
Thanks to Cisa patented Grazie Aquazero® technology, water consumption is extremely limited.
For the WSM versions, a simple water connection is sufficient to power the steam generator and a single electrical connection to power all the appliances.

THE IMPORTANCE OF TRACEABILITY SOFTWARE IN WASTE TREATMENT PLANTS:
ENHANCED SAFETY WITH TRACEWASTE MONITORING.
The innovative Cisa wsd® solution for treating hospital waste with the TraceWaste software carries out the complete waste traceability process. TraceWaste also makes it possible to protect facilities against waste management liabilities by ensuring maximum control over management and transport, simplifying the procedures for waste disposal. Cisa Group’s proprietary TraceWaste is recognised as a leading traceability software. |
